LED drivers are essential components in LED technology as they regulate power to LED lights, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. LED drivers function by converting higher-voltage alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC) at lower voltages, typically 12V or 24V. The central function of an LED driver is to match the electrical characteristics of the LEDs, providing a constant current to prevent issues like thermal runaway
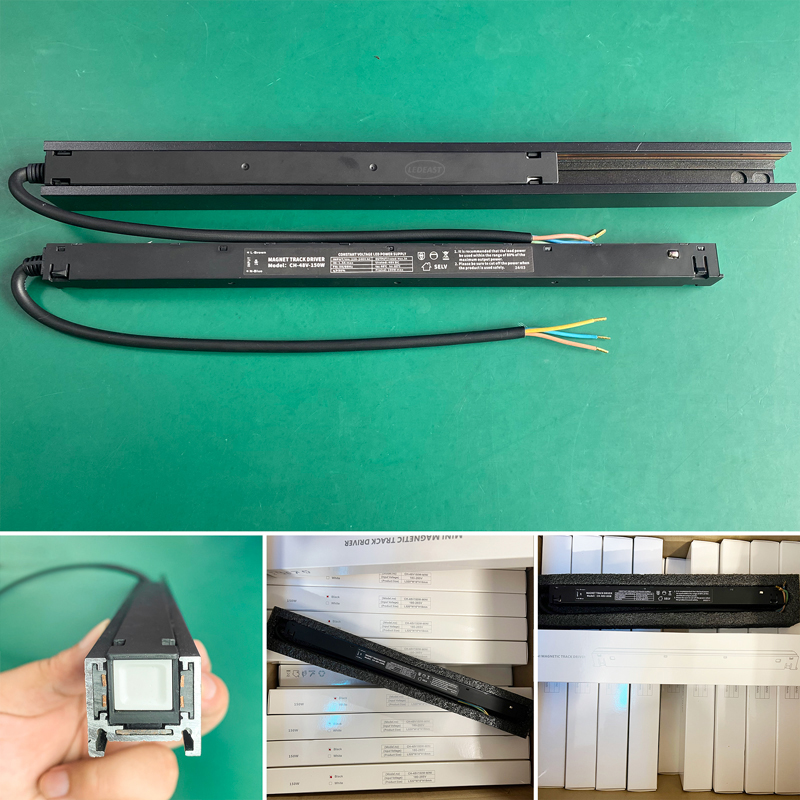


LED drivers come in various types, such as constant current and constant voltage drivers, with each serving specific needs based on the LED requirements and application scenarios. Constant current LED drivers maintain a steady current for the LEDs, ensuring consistent brightness, while constant voltage drivers vary current to maintain a steady voltage
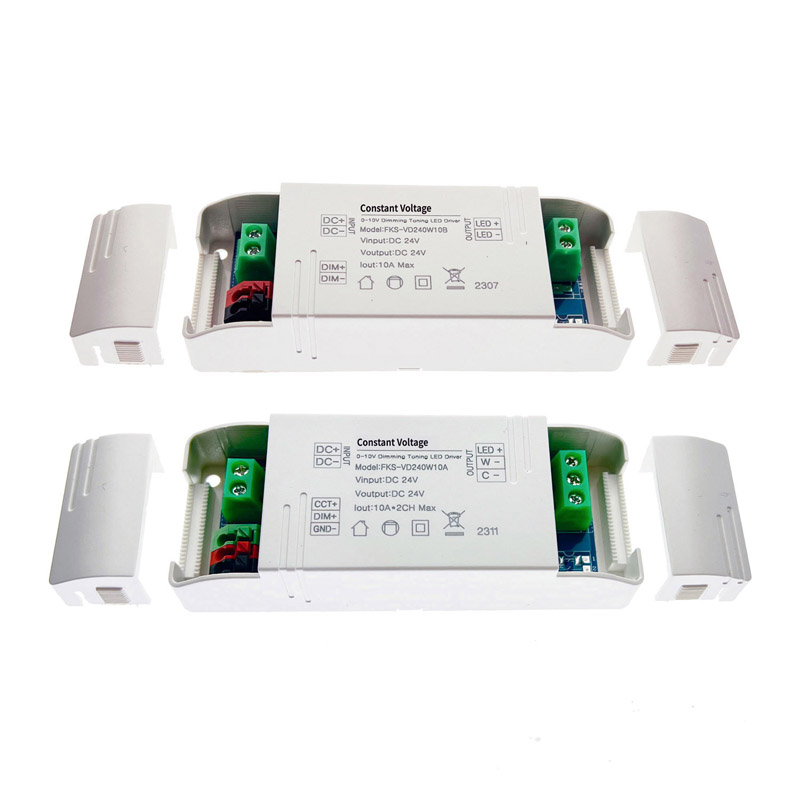


In terms of voltage, LED drivers can be low voltage DC drivers (5-36VDC) or high voltage AC drivers (90-277VAC). Low voltage DC drivers are recommended for smaller applications due to their efficiency and dimming options, while high voltage AC drivers are suitable for general lighting projects like residential or commercial lighting.
When selecting an LED driver, factors such as current and voltage mode, physical size, IP rating for environmental protection, power factor, maximum wattage, dimming capability, and compliance with safety standards are crucial considerations. It is important to choose the right LED driver to match the requirements of the LED lights being used to ensure optimal performance and longevity, especially in scenarios where high-power LED strip lights are employed.
In summary, LED drivers play a vital role in the functioning of LED lights by providing the necessary power supply while ensuring consistent performance and protecting the LEDs from damage caused by voltage fluctuations or excessive current.
Post time: Jun-22-2024


